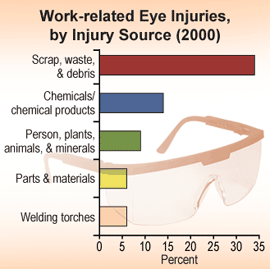
 About 2,000 workers seek medical attention for eye injuries every day. Over 600 of these injuries require an emergency room visit. The costs of an eye injury at work can add up quickly. Costs may include workers' compensation claims, medical expenses, lost production time, and the possibility of permanent blindness. There are several common causes for an eye injury at work, and learning them will help you improve your company's eye safety.
About 2,000 workers seek medical attention for eye injuries every day. Over 600 of these injuries require an emergency room visit. The costs of an eye injury at work can add up quickly. Costs may include workers' compensation claims, medical expenses, lost production time, and the possibility of permanent blindness. There are several common causes for an eye injury at work, and learning them will help you improve your company's eye safety.
Flying debris
Manufacturing and production workers move in an environment where eye hazards can come from all possible directions. Flying debris, the cause of most eye injuries, may come from tooling, cleaning, chemical compounds and maintenance projects. Flying debris can cause the following types of injuries:
- Eye abrasions can occur when debris enters your eye and rubs against the outer layers of your eye’s surface. This leaves scrapes and scratches on the soft surface and causes pain when you blink or touch the injured area. Without medical treatment, infections may complicate the eye's healing process.
- Eye penetration occurs where the debris penetrates your eye and remains lodged there, causing pain, burning, and possible loss of vision.
- Burning or itching eyes can occur when particles floating from machinery, ceilings and other materials in your work area land in your eyes. These particles cause abrasions and eye damage.
- Thermal burns
Welding causes thermal burns that can damage your eyes and the skin around them. The workers near you may also suffer thermal burns if they come too close without the proper protection. A welding helmet with a safety shield will protect you from an eye injury. Those around you will need safety glasses to protect them from sparks that cause thermal burns.
Chemical exposure
Chemicals are another potential hazard. Chemicals may splash into your eyes or the fumes from chemicals may cause burning and watering of the eyes. If either happens to you, immediately find the chemical’s Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and begin the emergency procedures for that chemical.
Not all chemical exposures require eyewash and the wash may do more harm than good. You must be aware of the emergency procedures for each chemical you work with. Make sure everyone knows where the MSDS sheets are located and how to read them. A binder holding the MSDS information should be readily accessible to all employees.
Preventing Eye Injuries
1. Eliminate the hazard wherever possible
When addressing potential hazards at your company, including eye hazards, we always recommend following OSHA's Heirarchy of Controls to find the highest order solution possible. Consider whether installing engineering controls or eliminating the hazard altogether through a change in the process is possible.
2. Wear proper eye protection
Wearing the proper safety equipment increases eye safety at work. Always wear Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA) approved eye protection, which may include.
- Safety glasses
- Wrap around safety glasses
- Face shields
- Hoods with respirators
- Safety goggles
3. Train your employees on the correct first aid procedures for each type of eye injury
Make sure your employees know the correct actions to take when an eye injury occurs and that eye washes are available and in good working order. Employees should know exactly what to do when an injury happens to avoid making matters worse.